Building the Configuration File
supersparrow is a standalone application that uses libsupersparrow to determine the POP closest to a given IP address. supersparrow accepts command line options and can be configured using a configuration file. The supplied /etc/supersparrow.conf configures supersparrow so that it can be run as a map from Apache's mod_rewrite. As this file contains potentially sensitive information, including the password to the route server, you should ensure that only the super user can read this file.
$ chmod 600 /etc/supersparrow.conf
The following directives in this file are of special note:
peer 64700=www.x.apache-test.supersparrow,64702=www.y.apache-test.supersparrow
This sets two peers with AS numbers 64700 and 64702. The hostname associated with each peer is www.x.apache-test.supersparrow and www.y.apache-test.supersparrow respectively. Note that hostnames are associated with peers as this will form part of the URL that apache redirects a client to.
batch
This sets supersparrow to read queries from stdin. Results will be printed to stdout. In this mode supersparrow will continue to run and wait for queries to be input to stdin both on startup and after each query is answered.
password frub
This sets the password that will be used to access the route server.
route_server zebra
This is used to tell supersparrow that the route server it will be contacting will run GNU Zebra.
self www.x.apache-test.supersparrow
This sets the default result, of no valid peer can be found,
to www.x.apache-test.supersparrow.
The configuration may be tested by running supersparrow
on the command line and entering queries to stdin:
To end the test use control-D. Any logs generated should
be logged to syslog, see notes
on logging for more details. To show information on
supersparrow's communication with the route server use
the -v command line option.
Again, to end the test hit control-D. The output shows that
there are two prefixes covering 192.168.193.13, and the prefix with AS
path 64702 is preferred. The PEERS: line shows that 64702 has
been configured as a peer and is associated with the hostname
www.y.apache-test.supersparrow, this is returned.
As supersparrow will be executed internally by
Apache it does not need to be configured to start at system boot.
For reference the resulting configuration file for
supersparrow is available.
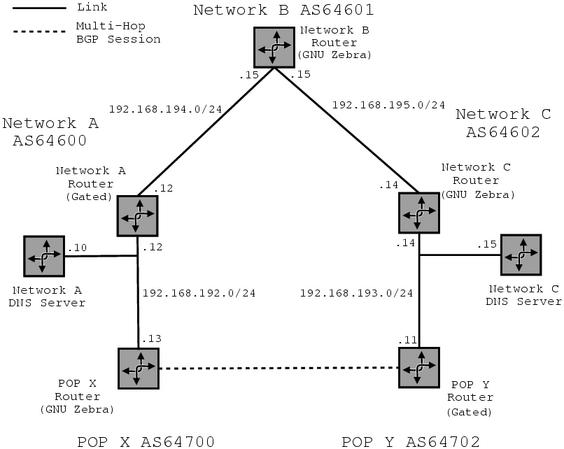
POP X Router:
/etc/supersparrow.conf.
A complete set of configuration files for this network setup
can be found here.
Copyright © 2000 HormsTesting
$ supersparrow
192.168.192.10
www.x.apache-test.supersparrow
192.168.193.13
www.y.apache-test.supersparrow
$ supersparrow -v
supersparrow version 0.0.0pre0 Copyright Horms
Logs sent to syslog
Hello, this is zebra (version 0.90.pre.horms.1)
Copyright 1996-2000 Kunihiro Ishiguro
User Access Verification
ÿûÿûÿþ"ÿýPassword:
jasmine> 192.168.193.13
sh ip bgp 192.168.193.13
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.193.0/24
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
64702
192.168.193.11 from 192.168.193.11 (192.168.193.11)
Origin IGP, metric 1, localpref 100, valid, external, best
Last update: Tue Oct 10 23:28:23 2000
64600 64601 64602
192.168.192.12 from 192.168.192.12 (192.168.192.12)
Origin IGP, metric 1, localpref 100, valid, external
Last update: Tue Oct 10 23:28:07 2000
jasmine>
PEERS: 64700=www.x.apache-test.supersparrow 64702=www.y.apache-test.supersparrow
ASPATH: 64702
www.y.apache-test.supersparrow
Configuration File
Notes on Commands
Commands shown in paragraphs of preformated text are prefixed by the shell
prompt $ to avoid confusion between commands and their output. An
instruction to run the command echo flim is formated as:
$ echo flim
flim
Last Updated: Tue May 17 17:37:17 2005

![[Sparrow]](../../pics/sparrow.gif)