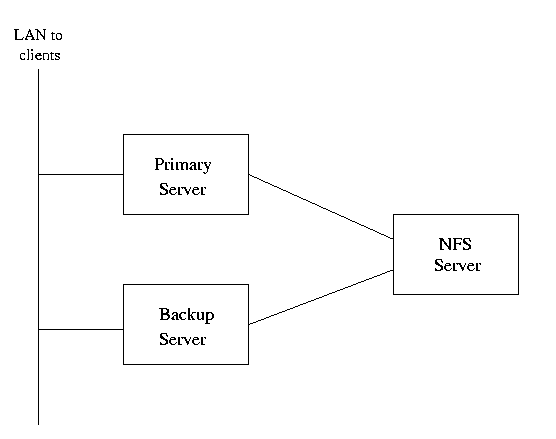
Figure 1: Replicated front end servers
NFS is an access mechanism. Briefly it enables files on one host to be mounted as part of the file system on another host. Although NFS itself is not redundant it does bear some investigation due to its wide spread implementation and some new developments that increase NFS performance.
An application of NFS which allows some form of redundancy without replication is shown in figure 1. The clients can be redirected to either the Primary of Backup server using mechanisms such as ARP spoofing [Hor98] or a layer 4 switch [Net98] which allows for session management of connections. This server can source its content from the NFS server. Hence the servers that clients see are redundant although the content itself is not replicated.
This is not an ideal situation as the NFS server is still a single point of failure and the current implementation of NFS in release kernels does have some performance problems. There is however hope as additional NFS servers can be maintained using a mechanism such as rsync for synchronisation as discussed in section 3. Additionally recent advancements in the NFS implementation have made significant inroads to the performance problem.